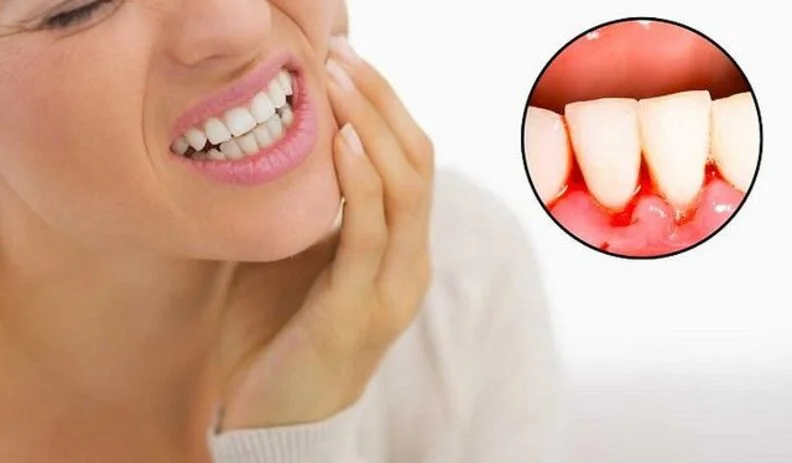
Gum bleeding is not just a minor or temporary symptom. In many cases, it can be a sign of an underlying oral or systemic condition that requires accurate diagnosis and proper treatment. At Al Safwa Medical Center in Bani Yas, Abu Dhabi, gum bleeding cases are approached with advanced dental standards, starting from detailed clinical evaluation to developing a tailored treatment plan based on internationally approved periodontal protocols.
This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the most common causes of gum bleeding, diagnostic approaches, and available treatment strategies, with practical insights into how our dental team addresses these cases for optimal outcomes.
What are the most common causes of gum bleeding?
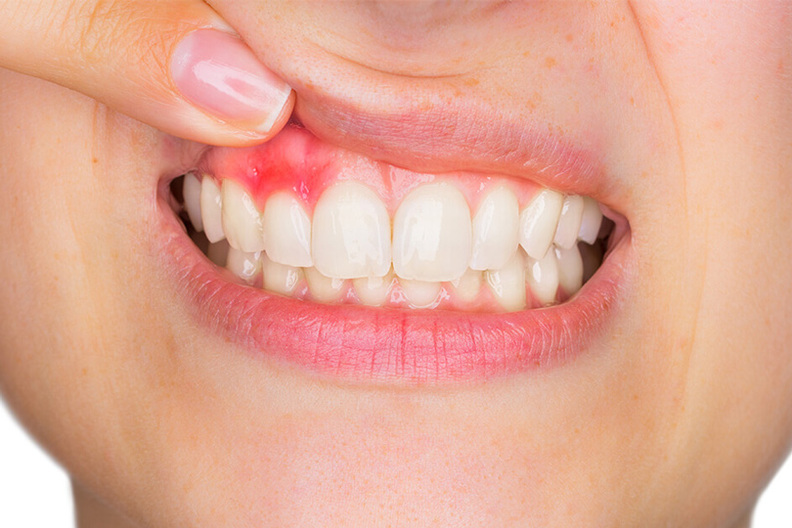
Gum bleeding can be caused by local factors in the mouth or by systemic diseases that affect the body’s ability to heal. The most common causes include:
- Gingivitis: The earliest stage of gum disease, usually caused by the buildup of bacterial plaque along the gumline. This plaque contains bacteria that irritate gum tissues, leading to redness, swelling, and bleeding when brushing or chewing.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced form of gum disease that affects the supporting ligaments and bone. This leads to persistent bleeding, gum recession, and tooth mobility.
- Aggressive tooth brushing or using a hard-bristled toothbrush: Excessive force or hard bristles can rupture small capillaries in the gum tissue.
- Vitamin deficiencies (especially Vitamin C and Vitamin K): Vitamin C deficiency weakens connective tissue, while Vitamin K deficiency affects blood clotting, both of which increase bleeding risk.
- Anticoagulant medications: Drugs such as warfarin or aspirin can make even minor gum injuries bleed more easily.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, puberty, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and reactive to bacterial buildup.
- Systemic diseases: Diabetes, liver disorders, and blood clotting disorders can all cause or worsen gum bleeding.
When bleeding changes from being occasional to persistent, a thorough clinical examination is necessary to identify the root cause before starting any treatment.
How is gum bleeding diagnosed at Al Safwa Medical Center?
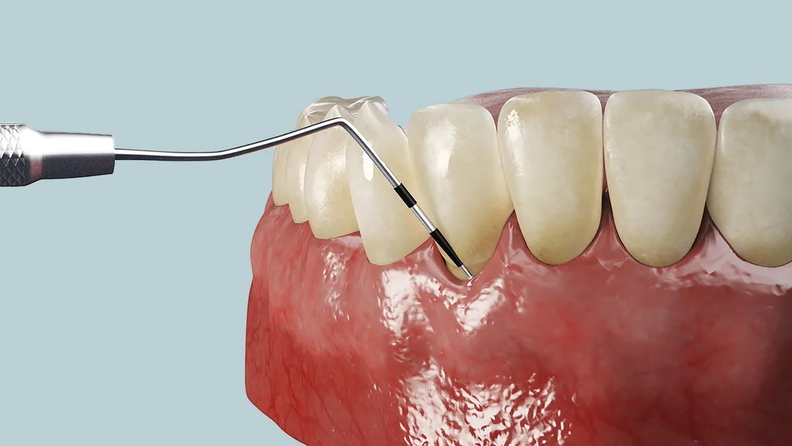
At Al Safwa Medical Center, gum bleeding diagnosis follows a thorough clinical protocol supported by advanced diagnostic tools to pinpoint the exact cause. Diagnostic steps include:
- Comprehensive medical history review: Understanding medications, chronic illnesses, and oral hygiene habits.
- Intraoral examination: Assessing gum color, texture, presence of pockets, or recession.
- Periodontal probing: Measuring gum pocket depth using a calibrated periodontal probe.
- Digital radiographs: Detecting bone loss and subgingival calculus.
- Laboratory tests: When systemic or nutritional causes are suspected, such as vitamin deficiencies or clotting disorders.
These steps help determine whether the bleeding is due to superficial inflammation treatable with a professional cleaning, or advanced periodontal disease requiring more extensive intervention.
What are the most effective treatment options for gum bleeding?
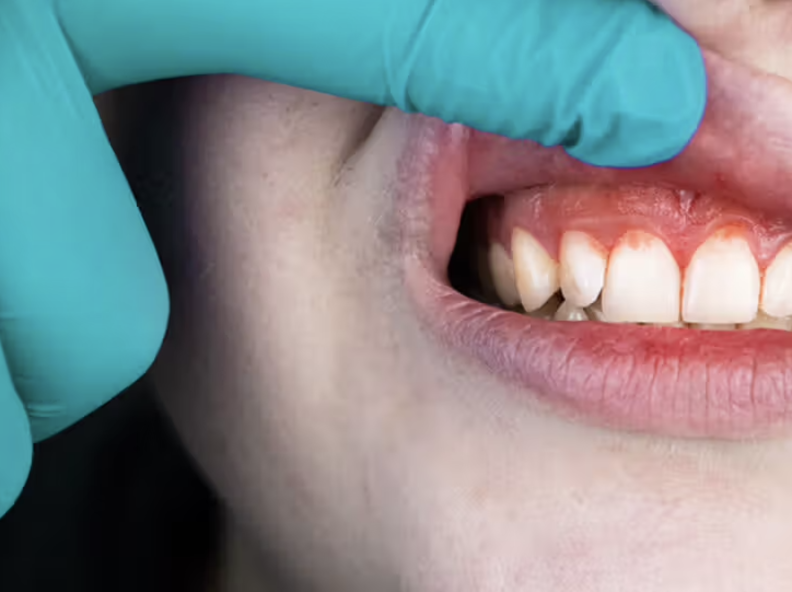
Treatment is always based on addressing the underlying cause while considering the patient’s overall health. At Al Safwa Medical Center, we offer:
1. Professional dental cleaning (scaling and polishing)
Plaque and tartar are removed from above and below the gumline using ultrasonic scalers or laser devices, followed by polishing to minimize bacterial buildup.
2. Periodontal therapy
Deep cleaning with root planing to remove bacterial deposits from deep gum pockets, promoting gum reattachment to teeth.
3. Laser-assisted periodontal therapy
A minimally invasive approach to sterilizing gum pockets and stimulating tissue healing, with reduced bleeding and post-procedure discomfort.
4. Medication-based therapy
Prescribing antimicrobial mouth rinses such as chlorhexidine or localized antibiotics when indicated.
5. Oral hygiene training
Educating patients on correct brushing technique, selecting a soft-bristled brush, and using fluoride toothpaste.
6. Surgical intervention if needed
Advanced cases may require flap surgery to reduce pocket depth or gum grafting to restore lost tissue.
7. Treating systemic causes
Coordinating with the patient’s physician to manage chronic diseases or adjust medications contributing to bleeding.
How can dental implants help after tooth loss due to gum disease?
When advanced gum disease leads to tooth loss, dental implants can restore both function and aesthetics. At Al Safwa Medical Center:
- We use Grade 4 titanium implants approved under international safety standards for maximum bone integration.
- Bone grafting is performed when bone loss is present to support the implant.
- Strict sterilization protocols are followed to minimize infection risk and ensure long-term success.
Implant placement is only considered after the gum disease is fully treated to prevent peri-implant infections.
What are the best prevention strategies for gum bleeding?
Prevention plays the most important role in maintaining healthy gums:
- Brush teeth twice daily using a soft-bristled brush and proper technique.
- Use dental floss daily to remove plaque between teeth.
- Visit your dentist every 6 months for a check-up and professional cleaning.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in Vitamin C and Vitamin K.
- Quit smoking as it worsens gum disease and delays healing.
These preventive steps significantly reduce the risk of gum inflammation and recurrent bleeding.
How to differentiate between temporary and chronic gum bleeding?
- Temporary bleeding: Usually caused by brushing too hard or minor trauma. It resolves in 2–3 days with proper oral care.
- Chronic bleeding: Occurs consistently and may be accompanied by bad breath, gum swelling, or tooth mobility. Often a sign of gum disease that requires immediate professional evaluation.
Knowing the difference helps patients decide when to seek professional care.
When should you see a dentist immediately?
Urgent dental consultation is needed when:
- Bleeding is heavy and does not stop.
- Bleeding is accompanied by severe pain and swelling.
- Post-surgical bleeding continues for several hours.
- Bleeding gums are associated with fever or extreme fatigue.
These signs may indicate advanced gum infection or systemic illness requiring prompt medical attention.
The role of Al Safwa Medical Center’s dentists in managing gum bleeding
Our team includes specialists in periodontology, oral surgery, and implant dentistry such as Dr. Mohammed Dalloul and Dr. Saleh Salem, with extensive experience in managing complex gum bleeding cases.
We combine:
- Accurate diagnosis using advanced digital tools.
- Laser techniques for effective tissue disinfection.
- Personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s medical and oral condition.
This comprehensive approach ensures both symptom relief and long-term gum health.
Conclusion
Gum bleeding can be an early warning sign of gum disease or deeper health problems. Addressing it early can prevent tooth loss and other complications. At Al Safwa Medical Center, we focus on accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and preventive care to maintain optimal oral health. For more information or to book an appointment, visit Al Safwa Medical.